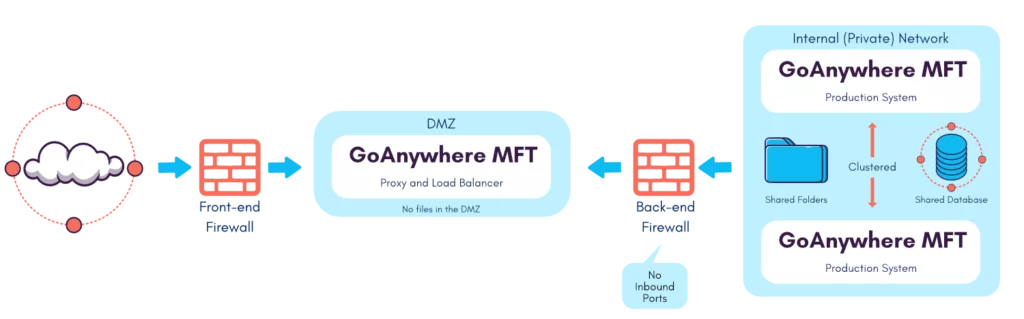
Typically, GoAnywhere Gateway is located within the DMZ and is installed in the private/internal network.
MFT creates an outbound connection to Gateway, which is used as a “control channel” for passing commands and messages between products. This control channel will initially provide the proxy details (IP and port mappings) to GoAnywhere Gateway.
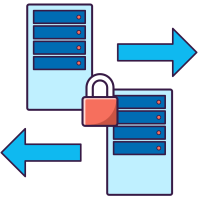
GoAnywhere Gateway is an enhanced reverse and direct proxy that provides organizations with an additional layer of security for data exchange with trading partners.
With GoAnywhere Gateway, file sharing services can be kept securely within your private network, without exposing sensitive data to your DMZ. Connections can be made to external systems on behalf of private network users.
The MFT solution works in any environment or operating system. GoAnywhere Gateway is a platform independent software solution. Install it on Windows, Linux, AIX, UNIX or other operating systems to enforce file security in the environment that works best for you.
As a forward proxy, GoAnywhere Gateway can establish connections to external systems on behalf of users and applications on the private network. This allows you to more easily manage file transfers from your firewall. In addition, the identities and locations of your internal systems are hidden for better security.

Files can be securely shared with business partners, users, customers, and vendors, while preventing critical documents or files from being stored, even temporarily, in your DMZ.
Your file servers (e.g., FTPS, SFTP, HTTPS, and AS2) can be kept securely within your internal network. This allows you to keep inbound ports to your network closed, which is essential to comply with data security standards such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, HITECH, SOX, ISO 27000 and GLBA.
Ask our experts to test GoAnywhere MFT and discover all the benefits of GoAnywhere Gateway.

Reverse Proxy
GoAnywhere Gateway acts as a "front end" and hides the use of folders as it does for services (FTP/S, SFTP, HTTPS). When trading partners need to exchange data with your company, they will be able to connect with GoAnywhere Gateway. GoAnywhere Gateway will then attach these two requests to the appropriate services on the private network. All additional data channels are opened from the private network and through GoAnywhere Gateway, requiring no inbound ports.
Forward Proxy
GoAnywhere Gateway will connect to external systems on behalf of users and applications on the private network. By routing requests through a central point with GoAnywhere Gateway, you can more easily manage your firewall forwarding more easily. For security purposes, the forward proxy hides the identities and location of your system.
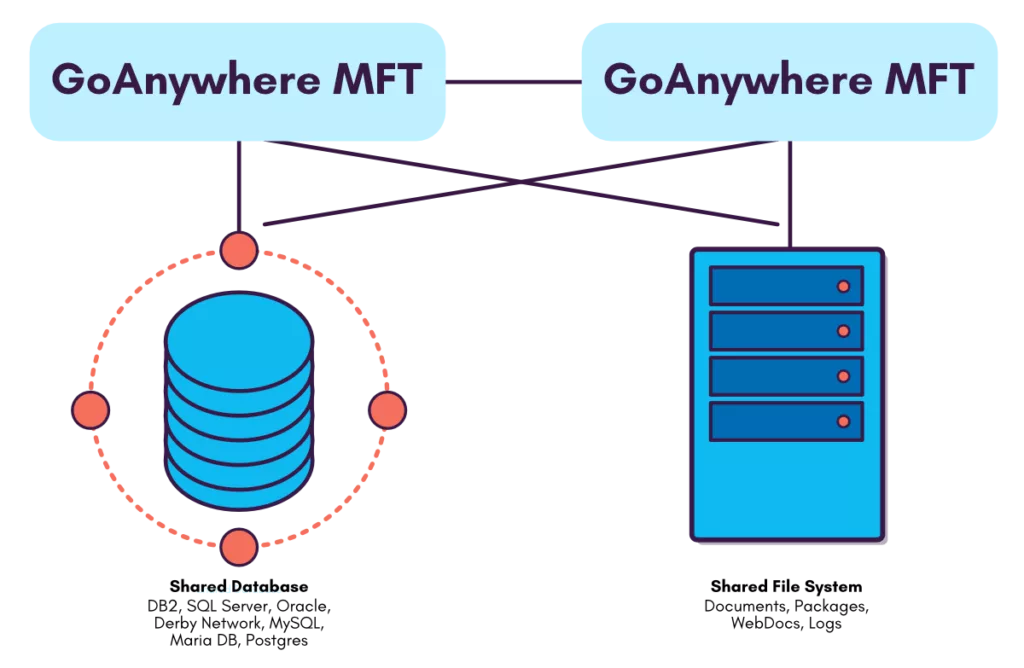
GoAnywhere Gateway can serve as a load balancer to distribute workloads among multiple GoAnywhere MFT installations within a cluster, as well as among other systems on your network.
If one system were to fail in the cluster, GoAnywhere Gateway would send all new trading partner connections to the other systems in the cluster.
This active-active structure provides greater availability for mission-critical environments.
FTP, FTPS, and SFTP will use the round-robin algorithm to load-balance connections across systems in the cluster.
For each new connection from a trading partner, GoAnywhere Gateway will distribute that session to the next FTP/FTPS/SFTP server (in sequential order) within the cluster.
This provides organizations with a high level of protection for shared file transfers between their systems, business partners, employees and the cloud.
HTTP/S is a stateless protocol that also uses the round-robin algorithm.
The HTTPS protocol defines the format of the messages through which Web browsers communicate and determines how a browser should respond to a Web request. It is a stateless protocol, which means that each instance of communication is treated as an independent event and no session information from previous requests is retained by the receiver.
This protocol allows each connection to the same HTTP/S server to be maintained to ensure session integrity.
This is important because the user's HTTP/S session can usually only be handled by one HTTP/S server at a time.
We use cookies to optimise your experience & our services on the website. Nous utilisons des cookies pour optimiser votre expérience et nos services.